miércoles, 14 de diciembre de 2016
Obsolescencia Programada
Aprende a ser un consumidor responsable. Mira cómo de curioso es el mundo de la producción de bienes de consumo en los vídeos y recursos de la página de RTVE.ES
Memoria de España: ¡Vivan las caenas!
Recomendación para estas Navidades y para cualquier tema de Historia de España que tengáis que estudiar este año, o en 2º de Bachillerato.
Sigue el siguiente link para ver el vídeo en la página de RTVE.ES
Sigue el siguiente link para ver el vídeo en la página de RTVE.ES
martes, 22 de noviembre de 2016
Nitosha's Revolution
Thanks NiTosha for giving us the American point of view on your very important revolution.
Comment this source:
"We the People of the United States, in order to form a more perfect union, establish justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America".
Comment this source:
"We the People of the United States, in order to form a more perfect union, establish justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America".
martes, 15 de noviembre de 2016
Ampliación: Juan Antonio Cebrián, Revolución Francesa
Extrae y desarrolla 4 hechos o curiosidades de la Revolución Francesa, que en nuestro libro sólo vienen mencionados o muy poco desarrollados.
Waterloo, 1815
Amplía los conocimientos de la importante Batalla de Waterloo a manos uno de los grandes expertos de la UNED:
La Revolución Francesa en Canal Historia
Repasa la unidad con este documental que se corresponde con parte de los contenidos de esta unidad:
Waterloo, by ABBA
This is one of the most popular songs of the 20th century, performed by the Swedish group ABBA. Explain what does it mean when someone use the phrase: "FINALLY FACING MY WATERLOO".
Lyrics:
My, my, at Waterloo Napoleon did surrender
Oh yeah, and I have met my destiny in quite a similar way
The history book on the shelf
Is always repeating itself
Waterloo - I was defeated, you won the war
Waterloo - Promise to love you for ever more
Waterloo - Couldn't escape if I wanted to
Waterloo - Knowing my fate is to be with you
Waterloo - Finally facing my Waterloo
My, my, I tried to hold you back but you were stronger
Oh yeah, and now it seems my only chance is giving up the fight
And how could I ever refuse
I feel like I win when I lose
Waterloo - I was defeated, you won the war
Waterloo - Promise to love you for ever more
Waterloo - Couldn't escape if I wanted to
Waterloo - Knowing my fate is to be with you
Waterloo - Finally facing my Waterloo
So how could I ever refuse
I feel like I win when I lose -
Waterloo - Couldn't escape if I wanted to
Waterloo - Knowing my fate is to be with you
Waterloo - Finally facing my Waterloo
How developed are you?

The HDI was created to emphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not economic growth alone. The HDI can also be used to question national policy choices, asking how two countries with the same level of GNI per capita can end up with different human development outcomes. These contrasts can stimulate debate about government policy priorities.
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development:
a long and healthy life,
being knowledgeable and
have a decent standard of living.
The HDI is the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions.
a long and healthy life,
being knowledgeable and
have a decent standard of living.
The HDI is the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions.
DOWNLOAD the 2015 HDI Report here and answer the following questions:
- Divide the world by HDI categories as it is in the table and define the upper and lower limits of each category. For example -- very high HDI from 0,8 to 1...
- Give 5 countries as an example per category.
- In which continent are those countries?
- How are different European countries distributed in terms of HDI?
sábado, 12 de noviembre de 2016
Duties of every Town Hall
As we are advancing through the unit, we are receiving popplets from students. This one has been made by Francisco Manuel Beret. Thank you very much!
viernes, 4 de noviembre de 2016
Socrative: Industrial Revolution
You can revise this unit by using our socrative.com test, with the following details:
IMPORT TEACHER CODE: SOC-25045135
Download the quiz in PDF here: DOWNLOAD
martes, 1 de noviembre de 2016
Theme Map of Europe
It's time to learn how to make a theme map. Use the blank political map of Europe provided by your teacher and also available in this post (HERE) and fill it with the data from the International Monetary Fund, published in Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_sovereign_states_in_Europe_by_GDP_(nominal)_per_capita.
First of all, write a title in capital letters stating what we are representing: "European countries by GDP per capita", for example. Do not forget to write the source of our data, normally down and on the side, and the date of our data: "IMF, 2014", for example.
Classify European countries by GDP per capita establishing 4 or 5 categories according to their values in the table. Each category needs a colour to represent their values. As we are representing quantitative values, colours may better have the same type but different intensity (all green or blue, but lighter or darker). This classification has to be placed on the map for everyone to read it properly. Use Russia as background in this case.
The following map is ONLY an example, because it's probably NOT using the same data as us:
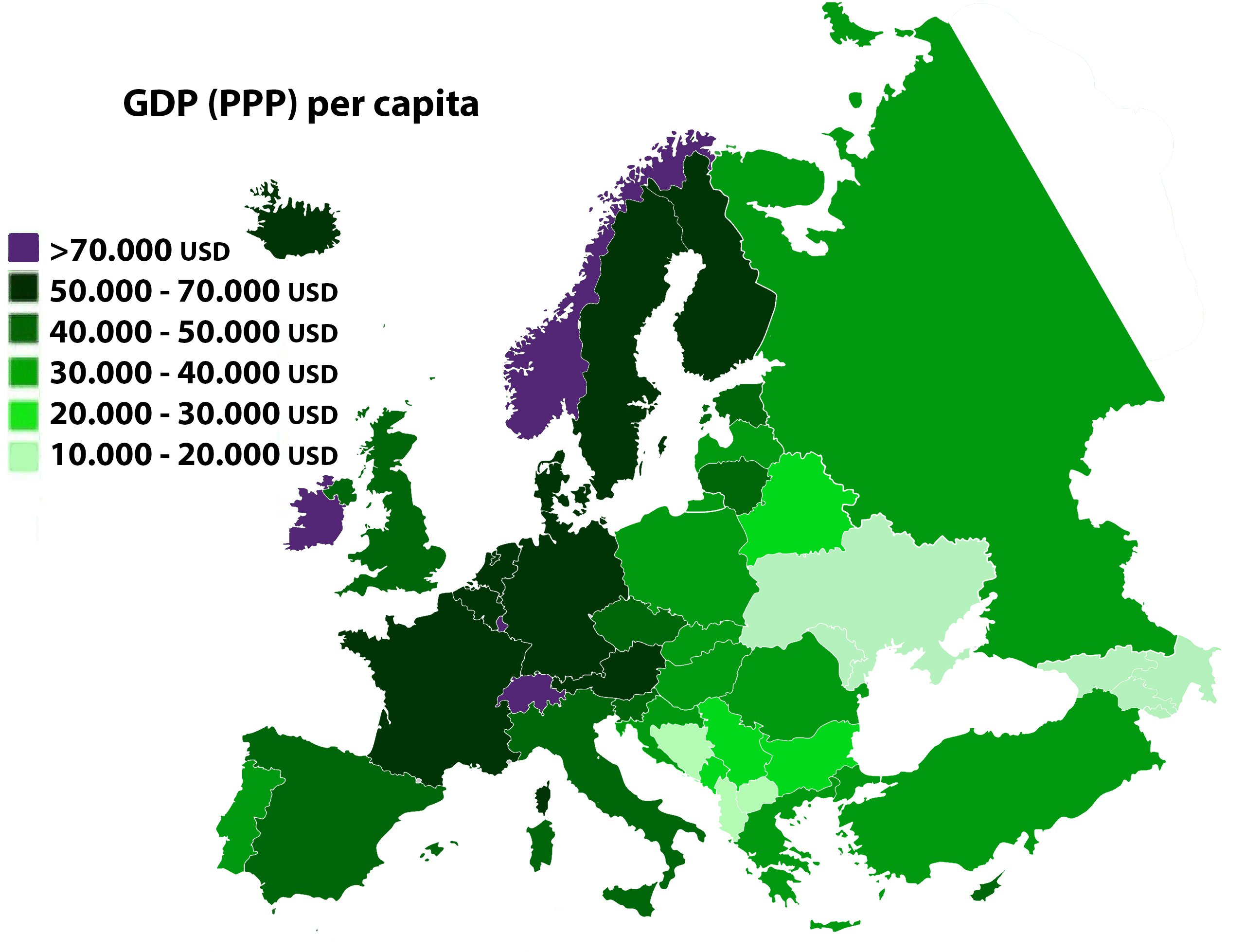
First of all, write a title in capital letters stating what we are representing: "European countries by GDP per capita", for example. Do not forget to write the source of our data, normally down and on the side, and the date of our data: "IMF, 2014", for example.
Classify European countries by GDP per capita establishing 4 or 5 categories according to their values in the table. Each category needs a colour to represent their values. As we are representing quantitative values, colours may better have the same type but different intensity (all green or blue, but lighter or darker). This classification has to be placed on the map for everyone to read it properly. Use Russia as background in this case.
The following map is ONLY an example, because it's probably NOT using the same data as us:

jueves, 27 de octubre de 2016
miércoles, 19 de octubre de 2016
PSOE is born
"El Partido Socialista Obrero Español se fundó clandestinamente en la taberna Casa Labra de Madrid, el 2 de mayo de 1879, en torno a 25 personas: 16 tipógrafos, cuatro médicos, un doctor en ciencias, dos joyeros, un marmolista y un zapatero. Encabezados por Pablo Iglesias, con lo que es el partido político más antiguo de España con funcionamiento ininterrumpido hasta la actualidad.
El primer programa del nuevo partido político fue aprobado en una asamblea de 40 personas, el 20 de julio de ese mismo año. Como partido obrero y de clase, el PSOE se adhirió a la II Internacional, que agrupaba a los partidos socialistas marxistas hasta su colapso ante la Primera Guerra Mundial.
El PSOE fue el segundo partido socialista y obrero que se fundó en el mundo (sólo el Partido Socialdemócrata de Alemania, SPD, se había fundado con anterioridad), celebrando su primer congreso en Barcelona en 1888. En dicho congreso se planteó una estrategia de lucha de clases. Durante él Pablo Iglesias afirmó que "La actitud del Partido Socialista Obrero con los partidos burgueses, llámense como se llamen, no puede ni debe ser conciliadora ni benévola, sino de guerra constante y ruda". En el Segundo Congreso del partido, en 1890, se decide la participación en las elecciones, aunque no se logró representación parlamentaria hasta el 8 de mayo de 1910, cuando la Conjunción Republicano-Socialista permitió a Pablo Iglesias obtener 40.899 sufragios y el título de diputado a Cortes".
Wikipedia en Español
- PSOE and their Trade Union, UGT, were born in the late XIX century. Why were they born so late?
- Does the name Pablo Iglesias sound familiar to you?
- Can you find any difference between the original idea of this party and today's ideology?
lunes, 17 de octubre de 2016
Reaction against Capitalism
Read the text and answer:
- Do you agree with the reaction of luddites? Does that make any sense?
- Do you know any Trade Unions in Spain today? What do they do?
Nota informativa: uso del móvil 3º ESO
Se informa a los padres de los alumnos de 3º de ESO, que se va a necesitar el uso del móvil en clase en la próxima sesión de esta semana para repasar la unidad del relieve en los grupos bilingües. Esto será el MIÉRCOLES 19 DE OCTUBRE.
Muchas gracias.
Muchas gracias.
Socrative: Changes in Ancient Régime
You can revise this unit by using our socrative.com test, with the following details:
IMPORT TEACHER CODE: SOC-24478652
Download the quiz in PDF here: DOWNLOAD
domingo, 16 de octubre de 2016
States of the World
From now on you have to study all the States that we can find in the World. To help you with this hard (and long) task I am going to recommend you some websites you may find useful. Don't worry, we are plenty of time and follow this path together during the whole academic year.
MAPAS FLASH INTERACTIVOS DE ENRIQUE ALONSO
Practice with one of the best geolocation sites on the web.

You better practice at home to compete in class against your teacher and your classmates.
GEOGUESSR
It is one of the most popular games in the Internet. It is about landmarks and landscapes identification, but it really helps with your geographic skills. Even the most famous youtubers play this game!!! Look:
MAPAS FLASH INTERACTIVOS DE ENRIQUE ALONSO
Practice with one of the best geolocation sites on the web.
You better practice at home to compete in class against your teacher and your classmates.
GEOGUESSR
It is one of the most popular games in the Internet. It is about landmarks and landscapes identification, but it really helps with your geographic skills. Even the most famous youtubers play this game!!! Look:
Follow the Leader!
Learning about the different political regimes of the World, let's stop for a moment and take a look at the less transparent one. The Kim Jong dynasty has spread North Korea with lies and fear. We are lucky to have some documentaries from the few visitors that can enter the country every year. See also how the population cried over the death of the previous leader:
Introduction to Political Geography
Read the following text and answer a few questions:
- Explain the difference between "State" and "Nations". Give examples in the World.
- Which elements constitute a State?
- Why is the European Union not a State like Spain?
Who is Adam Smith?
Adam Smith (1723-1790) was a Scottish philosopher and pioneer of political economy who set the rules and the theory of what is today capitalism.

In his work "The Wealth of Nations" he goes deep along 6 books through the concepts of:
- The Division of Labour,
- The term Productivity,
- and Free Market.
How are these term related to capitalism and explain the quotes below:

In his work "The Wealth of Nations" he goes deep along 6 books through the concepts of:
- The Division of Labour,
- The term Productivity,
- and Free Market.
How are these term related to capitalism and explain the quotes below:
Why the United Kingdom? A Peel speech:

Sir Robert Peel in Parliament, 1846.
- What do you think it would be an appropriate title for the text?
- According to the author, which physical and human factors favoured the industrial revolution?
domingo, 9 de octubre de 2016
How to comment a historical text
Texts are the main historical sources
that we are going to use in class. It is important to read and understand them
well because they are plenty of valuable information. Read carefully and underline
key words or sentences that will help you writing your commentary. Here are the
main guidelines to make the most of your work with them:
1/ INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION
Try not to start writing from the
middle of the historical process or facts. Introduce what you are going to do
and distribute your ideas properly. Remember, a good start can get the
attention of your teacher in a positive way!
In this section you should
mention the following points:
SOURCE: we have two options, PRIMARY OR SECONDARY,
o
PRIMARY SOURCE: What is a primary source?
Primary sources are materials directly related to a topic by time or
participation. These materials include letters, speeches, diaries, newspaper
articles from the time, oral history interviews, documents, photographs, artefacts,
or anything else that provides firsthand accounts about a person or event. For
example, a newspaper article about D-Day (which was June 6, 1944) written in
June 1944 was likely written by a participant or eyewitness and would be a
primary source.
o
SECONDARY SOURCE: Secondary sources are
works of synthesis and interpretation based upon primary sources and the work
of other authors. They may take a variety of forms. The authors of secondary
sources develop their interpretations and narratives of events based on primary
sources. An article about D-Day written in June 2001 probably was not written
by an eyewitness or participant and would not be a primary source, but a
secondary one, like any extract from your text book.
THEME: It represents the nature of the text. There is a wide
variety of themes, and you can even combine them.
o
DIFFERENT THEMES: The most common ones are Social
or Political themes. We can also find Religious, Economical, Literary, Legal, and
many others although they more difficult to find.
AUTHOR AND DATE: you can
find this two features stated, so lucky you. But, if not, you can still know
these facts by everything you have studied. For example, if you are reading
some article of the Treaty of Utrecht, you should know it was written in 1713.
And if the text talks about the separation of powers it may have been written
by Montesquieu, right?
2/ ANALYSIS
Now you have to go across the
document extracting the important issues you may find. Before heading to the ideas,
give your text a historical frame and place it in the right moment in history.
And now, the ideas:
MAIN IDEA: This is the message of the text. It may be written or
not, it is the sentence which summarizes all the information.
SECONDARY IDEAS: find important information which complements the
main idea. Follow the text structure and give some meaning to these ideas. They
may be important for explaining what is going on in the next section.
3/ EXPLANATION – HISTORICAL CONTEXT
Here is where you prove that you
have studied History. Here is where historical facts help us understand what
the text says. In chronological order:
CAUSES – BEFORE: What has happened in history before this source
that made it happen. In every unit you will be plenty of different causes for
many facts, so be accurate.
CONSEQUENCES – AFTER: our source can be so important that can
represent a big change in history. So, now is the moment in which we analyse
everything our source leads to.
4/ CONCLUSIONS
In this section, we are going to
close our commentary talking about the relevance of the analysed source, in two
different moments:
IMPORTANCE THEN: What did these facts changed and how important
were they in that moment in history.
IMPORTANCE FOR TODAY: Whatever we have seen in the text may still
have importance now. Following the same example of the Treaty of Utrecht,
Gibraltar is still British territory. Remember, we study history to explain why
the things are like they are today.
AVOID
- Repeating or copying exactly what is written in the text.
- Going back hundreds of years in time looking for causes.
- Explaining something you have studied only because you know that very well.
viernes, 7 de octubre de 2016
Montesquieu: The Spirit of Laws
Text: Montesquieu: The spirit of the laws, 1748
Activities:
1) Classify the text following the instructions we have worked on class (nature of the text, location, author, etc.)
2) Analyse the text (topic, main ideas, secondary ideas).
3) Historical context and conclusion (period, backgrounds and consequences, assessment of the text, and final summary).
4) Who represents each of these powers in a democratic regimen?
5) Extension activity: make a mind map with the app Popplet (popplet.com) with the current organization of the three powers mentioned by Montesquieu in the Spanish state.
“In each state there are three sorts of powers: legislative power, executive power over the things depending on the right of nations, and executive power over the things depending on civil right.
By the first, the prince or the magistrate makes laws for a time or for always and corrects or abrogates those that have been made. By the second, he makes peace or war, sends or receives embassies, establishes security, and prevents invasions. By the third, he punishes crimes or judges disputes between the individuals. The last will be called the power of judging, and the former simply the executive power of the state.
When legislative power is united with executive power in a single person or in a single body of the magistracy, there is no liberty, because one can fear that the same monarch or senate that makes tyrannical laws will execute them tyrannically.
Nor is there liberty if the power of judging is not separate from legislative power and from executive power. If it were joined to legislative power, the power over the life and liberty of the citizens would be arbitrary, for the judge would be the legislator. If it were joined to executive power, the judge could have the force of an oppressor.
All would be lost if the same man or the same body of principal men, either of nobles, or of the people, exercised these three powers: that of making laws, that of executing public resolutions, and that of judging the crimes or the disputes of individuals.”
Activities:
1) Classify the text following the instructions we have worked on class (nature of the text, location, author, etc.)
2) Analyse the text (topic, main ideas, secondary ideas).
3) Historical context and conclusion (period, backgrounds and consequences, assessment of the text, and final summary).
4) Who represents each of these powers in a democratic regimen?
5) Extension activity: make a mind map with the app Popplet (popplet.com) with the current organization of the three powers mentioned by Montesquieu in the Spanish state.
martes, 4 de octubre de 2016
Notes for "Changes in Ancient Régime"
These are your teacher Maria Delgado's notes about the unit we have just studied. Use it for personal study, together with your class notes and every activity we have done, and all the resources of this blog.
Maria Delgado: Changes in Ancient Regime
Maria Delgado: Changes in Ancient Regime
Review of Unit 1: Natural Landscapes

You can revise this unit by using our socrative.com test, with the following details:
IMPORT TEACHER CODE: SOC-21193485
Download the quiz in PDF here: DOWNLOAD
martes, 27 de septiembre de 2016
Uso del móvil en clase
Este año vamos a utilizar un amplio abanico de recursos digitales en clase, incluído el smartphone. Para ello, eventualmente y como excepcion por uso didáctico, los alumnos tendrán permiso para traer el móvil a clase el día seleccionado.
Una de las aplicaciones que vamos a utilizar es SOCRATIVE. Es una aplicación gratuita y ocupa y consume poco en el móvil.
Las actividades, una vez realizadas, serán compartidas en el blog para que puedan ser reutilizadas en casa, o por cualquier otro profesor.
Una de las aplicaciones que vamos a utilizar es SOCRATIVE. Es una aplicación gratuita y ocupa y consume poco en el móvil.
Las actividades, una vez realizadas, serán compartidas en el blog para que puedan ser reutilizadas en casa, o por cualquier otro profesor.
domingo, 25 de septiembre de 2016
Blank Physical Maps
Even if you are in possession of blank maps provided by your teacher, you can download the same maps from the following link to practice at home:
LINK TO BLANK SCANNED MAPS
sábado, 24 de septiembre de 2016
Top of the World
Welcome to the Hall of Fame of geographical features. Look for the champions of nature in our planet:
- The highest peak in Africa:
- The hottest desert in the World:
- The largest island in Africa:
- The longest river in the World:
- The largest lake in Africa:
- The Southernmost tip of Africa:
- The highest mountain range in the World:
- The highest peak in the World:
- The lowest country in the World:
- The largest inland sea in the World:
- The longest river in Asia:
- The deepest lake in the World:
- The highest plateau in the World:
- The longest mountain range in the World:
- The highest peak in North America:
- The highest peak in South America:
- The driest desert in the World:
- The largest island in America:
- The largest island in the Caribbean:
- The largest river by discharge (flow) in the World:
- The longest river in North America:
- The highest peak in Europe:
- The largest island in Europe:
- The largest island in the Mediterranean Sea:
- The longest river in Europe:
- The largest lake in Europe:
Charles III, the best major of Madrid
One of the best kings of Spain, and by far the best for the city of Madrid. Charles III (reign 1759-1788) came from Naples bringing with him the ideas of Enlightened Despotism: "everything for the people, but without the people".
From Habsburgs to Bourbons
The 1st of November of 1700, Charles II of Habsburg dies in Madrid without any sons or daughters. Our very ill king wrote in his testament that his French cousin Philip, Duke d’Anjou would be the next king of Spain. In a context of instability and crisis in Spain, important countries of Europe wanted to place their candidates in the Spanish throne. So, while France supported Philip, the grandson of Louis XIV, Great Britain and other allied countries supported other candidate, the Austrian Archduke Charles, son of the Holy Roman Emperor, also Charles II’s cousin.
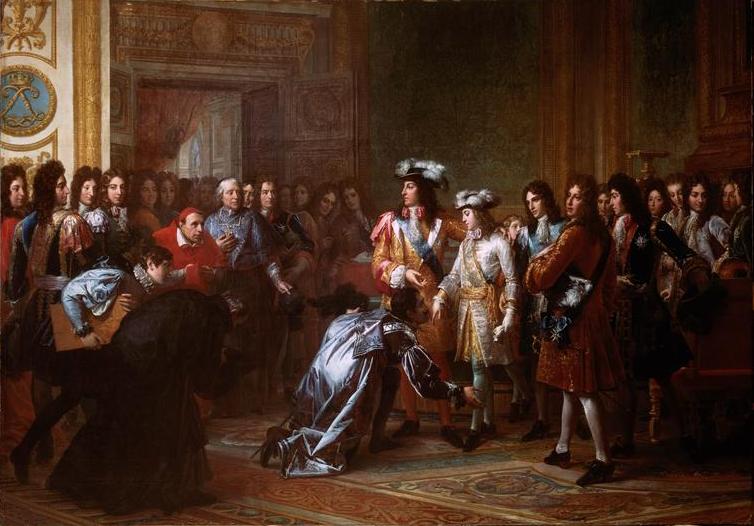

Proclamation of Philip V (1700. Versailles, France)
The War of the Spanish Succession had a double aspect: European and Spanish. This war started in 1701 and finished officially in 1714. Supporters of the Archduke Charles of Habsburg were mainly:
- The Crown of Aragon (fearing Philip's French centralism),
- The Holy Roman Empire,
- The United Kingdom,
- The United Provinces,
- Savoy,
- Portugal,
Supporters of the Duke d’Anjou (Bourbon) were mainly:
- The rest of Spanish territories,
- France,
- Bavaria,
- Naples, Sicily and Sardinia.

In 1711 everything changed. Something happened that made the end of the war come closer. The Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire died and also his successor to the throne, Archduke Charles’ older brother. So Charles was going to be king of Austria and also Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. That fact made England think that the balance of power could change to the other way if Charles becomes the king of Spain. As the probable winners of this war, they imposed certain conditions to Philip (France and Spain) to recognise him the king of Spain in the Treaty of Utrecht (1713), like for example:
- Philip V renounces to his rights to the French throne,
- Britain gets important trading benefits with Spanish America (slaves),
- Great Britain gets Gibraltar and Menorca, and from France, some Canadian and Caribbean territories,
- Savoy gets Sicily,
- Austria gets the remaining Spanish Flanders, Naples, Milan and Sardinia,
With those conditions everyone was happy, the allied countries and Philip. Everyone? No... Remember the Kingdom of Aragon? They were in Philip’s hands, thirsty of revenge. Philip took over these territories and imposed a terrible centralist policy based in the laws of Castile over Aragon, Catalonia, Valencia and Majorca. That is something that he didn’t do in the Basque Country and Navarre, as the supported him.
Sociedades Económicas de Amigos del País
The Enlightened Despotism with Charles III in Spain brought the application of knowledge in science and the foundation of regional societies which worked for the good and advance of agriculture, avoiding as much as possible the risks of hunger, accomplishing the principle of happiness for the population.
That was not exclusive from Spain, as other European countries had similar institutions. So,
- Can you tell me if there was one in Lucena and when was it founded. Extra information, such as location and minister in charge will be very much appreciated.
- Which economic principle of the Enlightment was promoted with this kind of institutions? Why was agriculture so important?
Viva la Vida: Coldplay and the end of Absolutism
You may know this song but you might not be aware that it was about the consequences of applying the ideas of THE ENLIGHTMENT. The 18th Century finished in France in a revolution that changed the World and History, leading the way to the Modern Era.
Lyrics and questions:
VIVA LA VIDA BY COLDPLAY AND THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
(1) I used to rule the _____________
Seas would rise when I gave the word
Now in the morning I sweep alone
Sweep the streets I used to own
(2) I used to roll the ______________
Feel the fear in my enemy's eyes
Listen as the crowd would sing:
"Now the old king is dead! Long live the king!"
(3) One minute I held the key
Next the walls were ___________ on me
And I discovered that my castles stand
Upon pillars of salt and pillars of sand
I hear Jerusalem bells a ringing
Roman Cavalry choirs are singing
Be my mirror my ____________ and shield
My missionaries in a foreign field
For some reason I can't explain
Once you go there was never, never an honest word
That was when I ruled the world
(Ohhh)
(4) It was the wicked and wild wind
Blew down the doors to let me in.
Shattered windows and the sound of _____________
People couldn't believe what I'd become
(5) Revolutionaries wait
For my _______________ on a silver plate
Just a puppet on a lonely string
Oh who would ever want to be king?
I hear Jerusalem bells a ringing
Roman Cavalry choirs are singing
Be my mirror my _____________ and shield
My missionaries in a foreign field
For some reason I can't explain
I know Saint Peter won't call my name
Never an honest word
But that was when I ruled the world
(Ohhhhh Ohhh Ohhh)
I hear Jerusalem bells a ringing
Roman Cavalry choirs are singing
My missionaries in a foreign field
For some reason I can't explain
I know Saint Peter won't call my name
Never an honest word
But that was when I ruled the world
-
PLEASE PAY ATTENTION TO THIS SONG. FILL IN THE GAPS AND ANSWER TO THE
FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:
(1)
Who would it be the narrator of
the song? Why?
(2)
Explain parts 1, 2, 3, 4 and
5.
Welcome Message 2016-2017
Welcome to our blog. This will be a very useful tool throughout this 2016-2017 academic year. We start in Lucena in the First Term, so let's rock this!
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)






